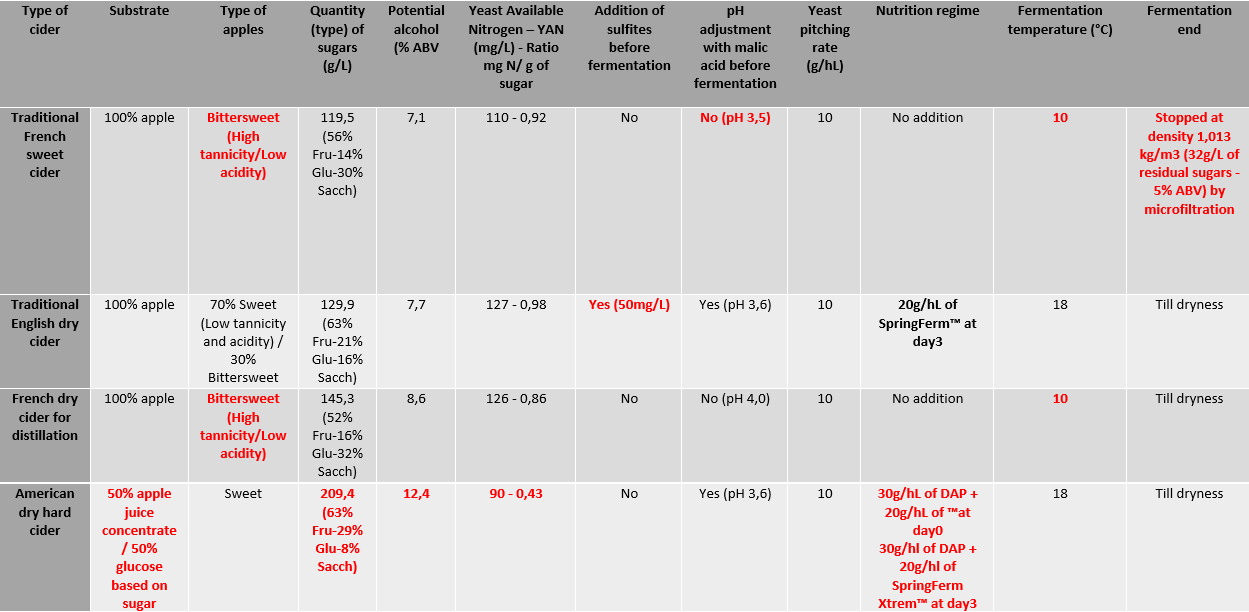
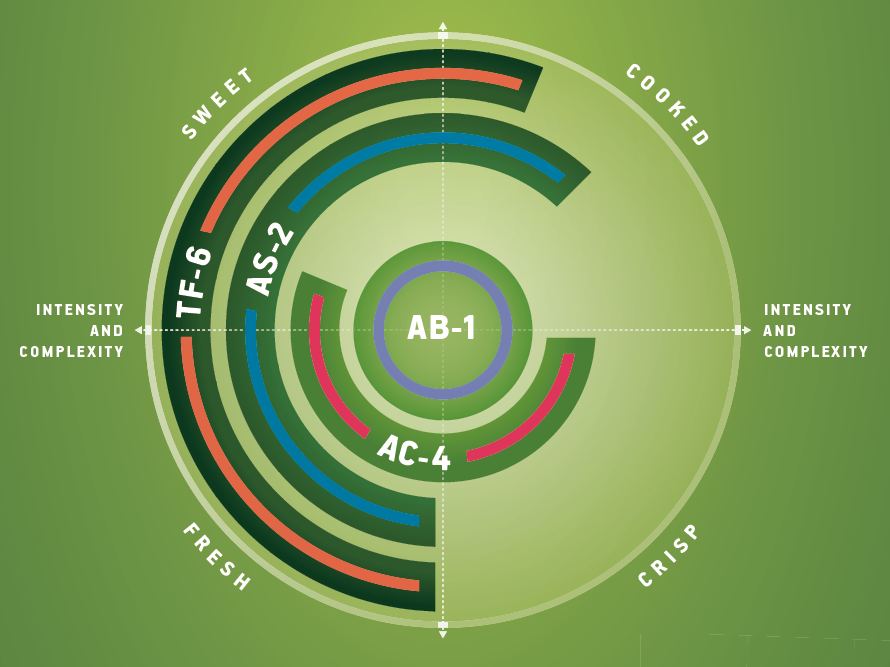
To assess the robustness of the strains towards difficult fermentation conditions, i.e. high sugar concentration (and content in the most difficult to assimilate fermentable sugars, i.e. fructose), low pH, nutrient deficiency, low temperature… Figure 1 shows the kinetics as well as the remaining sugars at the end of the fermentation in the hard cider.
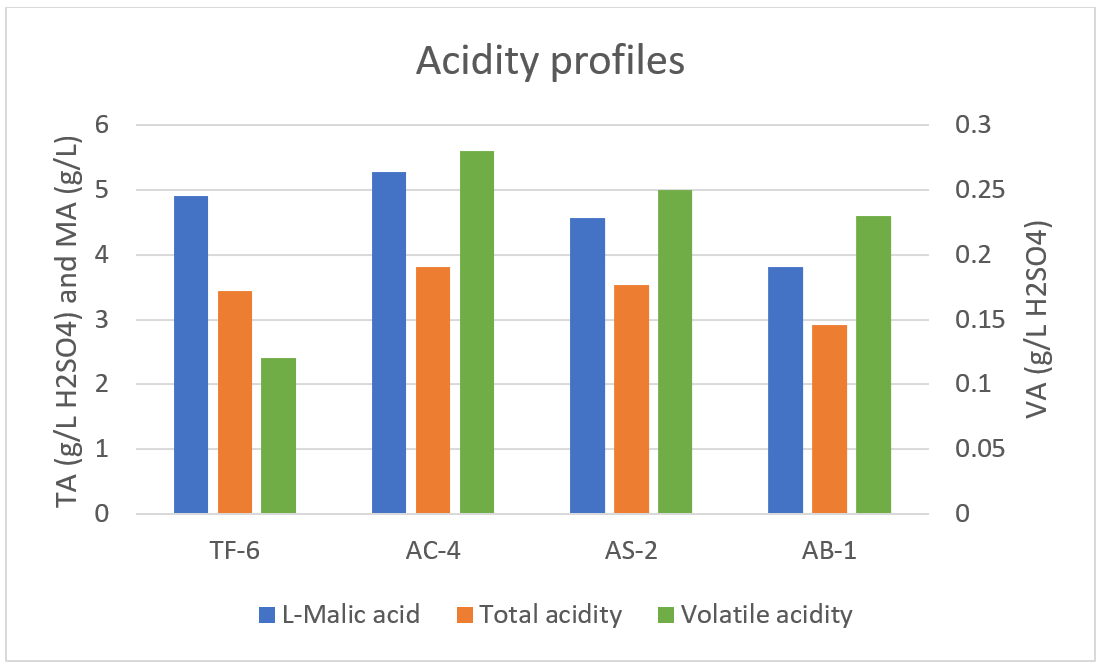
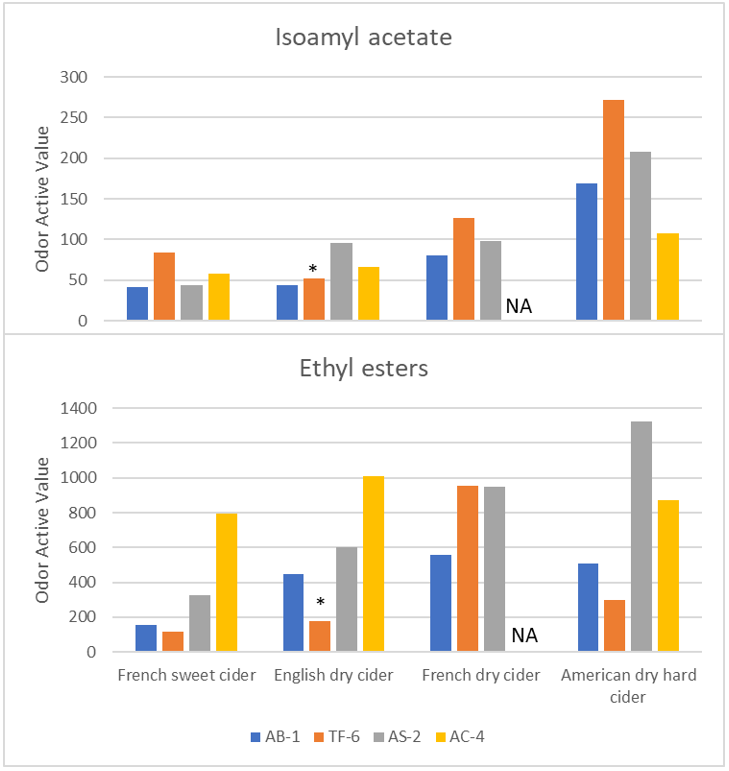
The strain SafCider™ TF-6 clearly stands apart from the other strains as it was not able to finish the fermentation and typically left ~25 g/L of sugars, among which fructose was a major part. This feature was observed in most of all matrices, as TF-6 was only able to finish the fermentation till dryness in the English cider (high YAN, low tannicity, then less inhibition and more O2 availability, high temperature), highlighting the bigger needs of this particular strain and the fact that the selection can be crucial depending on the cidermaker target. A higher sensitivity to high concentration of SO2 (50 mg/L maximum) is as well to be noticed for this strain.
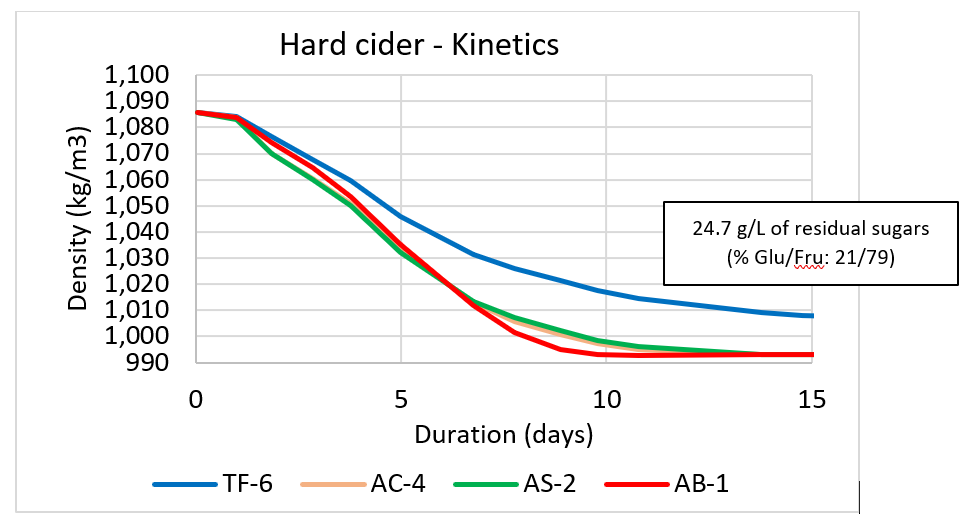
Fig.1 Kinetics follow-up through the American hard dry cider recipe.